CASE STUDY #1725 | REMAP
Precision Assembly of Automotive Belt Tensioners with Promess REMAP
CHALLENGE
Manufacturing automotive belt tensioners requires a highly coordinated assembly system that can precisely control both linear and rotational movements in real time.
Assembly Process
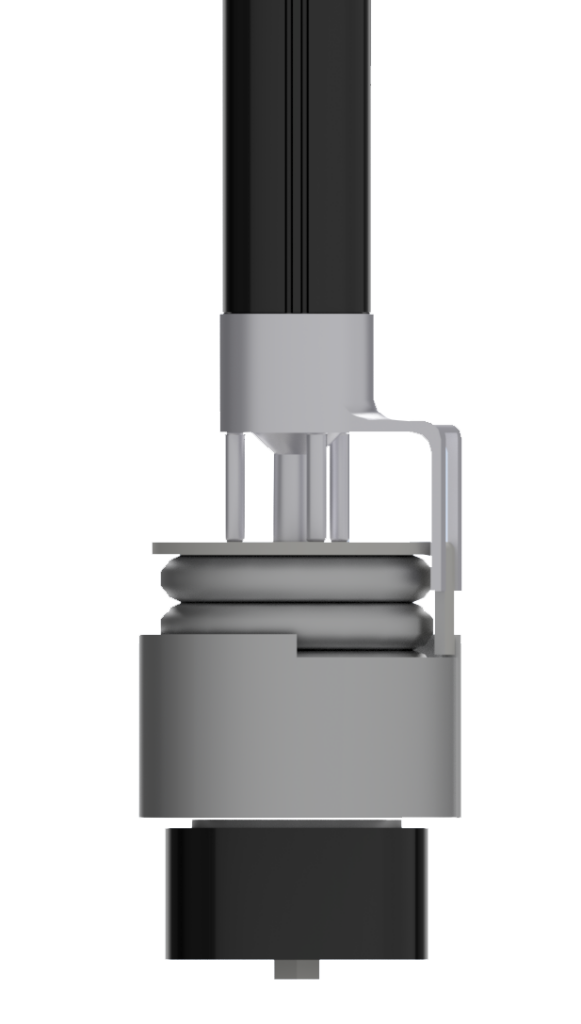
- The tensioner consists of a spring inside a housing which must be wound either to a specified location or to a specified torque.
- Once the spring is positioned inside the housing the linear actuator presses everything together with a controlled force that is light enough to allow the spring to turn while still being sufficient to hold the assembly together.
- At that point, the rotary axis is actuated to wind the spring to the specified position or torque, depending on the model being assembled.
- Control is then returned to the linear axis which applies enough force to hold the assembly together while a riveting head seals the finished tensioner.
- The final step is a controlled “unwinding” of the spring by the rotary axis to return the assembly to the “home” position without allowing the spring to snap back violently and potentially damage the completed tensioner.
Performing this assembly process with discrete rotary and linear actuators creates a very difficult control system design challenge. The manufacturer brought the process to Promess and worked with the engineering team to design a solution.
SOLUTION
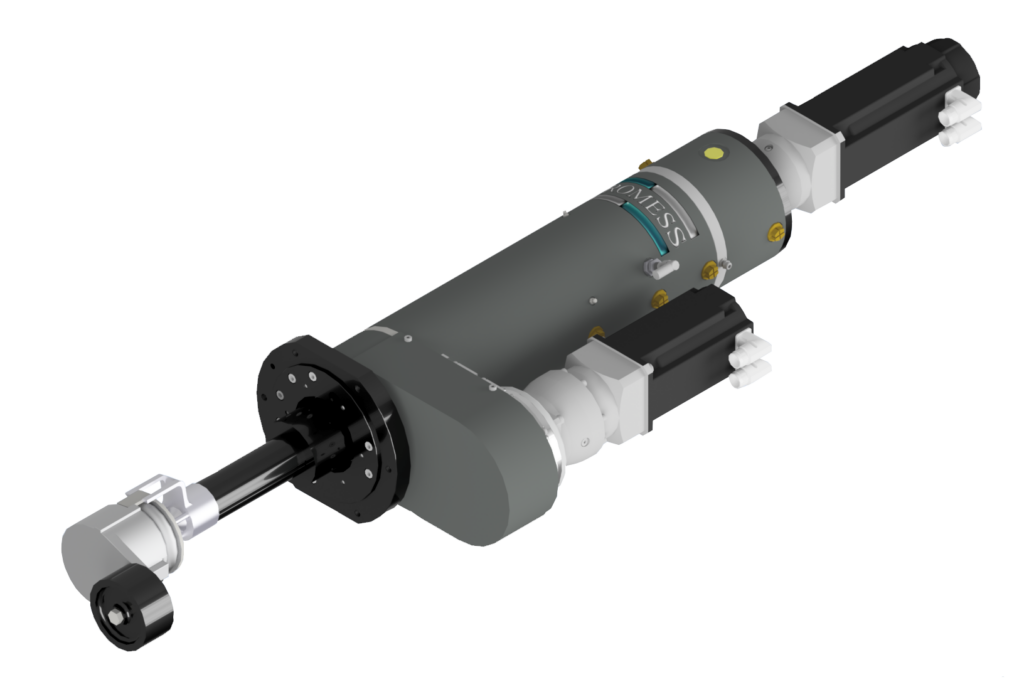
The manufacturer implemented the Promess Rotational Electro-Mechanical Assembly Press (REMAP), an fully programmable advanced servo-controlled system that integrates both linear and rotational motion within a single device. The REMAP solution provided:
Coordinated Motion Control
Coordinated Motion Control – The system seamlessly transitioned between linear pressing and rotational winding, ensuring each step in the assembly sequence was performed with precision.
Intelligent Force & Torque Monitoring
Integrated force, position, torque and angle sensors allow the REMAP to determine when the initial holding force has been reached, then wind the spring to its specified torque or position.
Automated Program Storage
The Promess motion controller stored multiple assembly programs, accommodating different belt tensioner models with varying winding characteristics.
Safe Spring Unwinding
The servo-controlled rotary axis unwound the spring in a controlled manner, preventing violent snap-backs that could damage the final assembly.
Data Collection & Traceability
Every assembled part was recorded and stored, allowing full traceability for quality control and future analysis.
RESULTS
By implementing the Promess REMAP, the manufacturer achieved:
- Consistent, High-Precision Assembly – Each belt tensioner was produced to exact specifications, reducing defects and ensuring long-term product reliability.
- Simplified System Integration – Using a single, pre-engineered system eliminated the need for multiple discrete actuators and the complexity of inter-system communication.
- Improved Manufacturing Efficiency – The streamlined process reduced assembly time while enhancing repeatability and quality control.
- Enhanced Traceability & Quality Assurance – The built-in data collection system provided a detailed record of each part, ensuring full process traceability for compliance and continuous improvement.
The Promess REMAP system transformed the assembly process for automotive belt tensioners, providing a reliable, fully integrated, and highly accurate solution. By combining servo-controlled rotary and linear motion, the manufacturer eliminated system inefficiencies, reduced scrap rates, and streamlined production.
This case study highlights the critical role of intelligent motion control in modern manufacturing—ensuring precision, efficiency, and traceability for high-performance automotive components.